Timeclock Hosts / IP Whitelists to Designate Company Facilities
How to configure the timeclock hosts (aka IP whitelist) in order to restrict clock-ins to company facilities.
AngelTrack's timeclock requires employees to be physically present at one of your stations in order to clock in and out. This document describes how AngelTrack knows whether your employees are at one of your stations.
This system is also used to restrict high-access security roles (Dispatcher, Supervisor, Biller) to company facilities, by means of the ☑ Provisional mark. Read the Roles and Permission Guide to learn more.
How Does AngelTrack Know Employees are Present at a Station?
You may be wondering whether AngelTrack uses GPS locations to decide whether employees are present at a company station.
The answer is no, it does not use GPS locations, because those can be easily spoofed using a web browser's F12 developer mode. Additionally, some computers and mobile devices do not have GPS at all. So GPS is not suitable for this purpose.
Instead of checking GPS, AngelTrack decides whether employees are present by checking something that cannot be spoofed: their IP address.
Because AngelTrack lives on the internet, it can see the IP address that each employee is using to reach the internet. By comparing these IP addresses to the list of your stations' IP addresses, AngelTrack knows which employees are connecting through one of your stations. Since the employee must be physically present in order to do that, this is a suitable qualification for using the timeclock.
For this to work, you must tell AngelTrack the IP addresses of your stations.
Employees can use their smartphones to clock-in and -out
Once an employee's smartphone has connected to a station's WiFi network, the smartphone's internet access makes use of the station's IP address. AngelTrack will therefore allow the smartphone to clock-in and -out.
As soon as the employee departs the station, their smartphone must disconnect from the station's WiFi, and once that happens, AngelTrack will no longer allow clock-in and -out.
"Why not use geolocation / geofencing of employee mobile devices?"
The reason why AngelTrack's timeclock does not utilize geolocation of employee mobile devices -- also known as "geofencing"-- is because geolocation data is easily spoofed.
By downloading certain mobile apps intended for developers, users can cause their mobile devices to report a false geolocation, which would allow them to clock-in and -out while not actually at your station.
Whereas AngelTrack's system, requiring the user to be connected to a station's wifi, cannot be spoofed, not even by highly technical users.
Add All Your Stations to the List
From the Settings page, click the "Timeclock Hosts" item to access the list of timeclock hosts. You must have Administrator, Captain, or HR privileges to proceed.
The list of timeclock hosts specifies the IP addresses (or ranges of addresses) from which employees are permitted to clock-in and -out. Specify the internet-facing addresses of your headquarters and all of your stations, so that employees can clock-in and -out at those locations using their mobile device, or by using a computer connected to the station's LAN.
This screenshot shows a fully configured timeclock: the "allow any address" entries are disabled, and each company building has an entry:
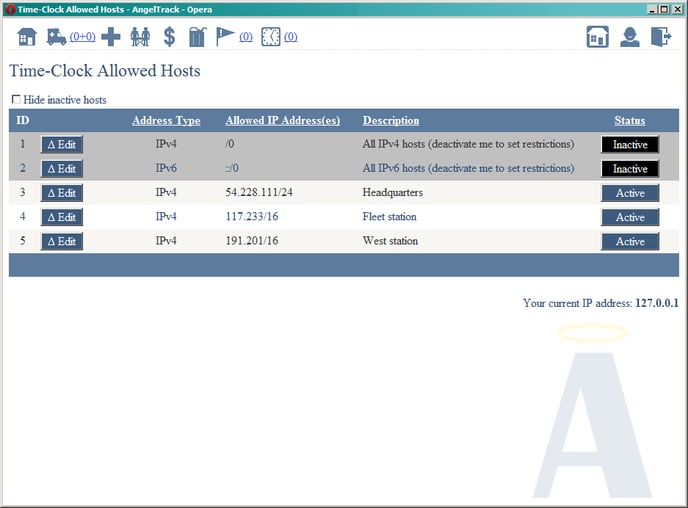
Once that's done, all workstations and mobile devices that are connected to those networks will permit clock-in and -out.
Being physically present inside the company building is not enough; workstations and mobile devices must be connected to one of the listed networks.
If you want to add a station's IP address to the list, but you don't know its IP address(es), then visit the station and perform the following steps. You can also call someone at the station and perform these steps for you, reading the results back to you over the phone:
- Select a computer or mobile device residing at the station.
- Use the computer or mobile device to connect to the station's WiFi.
- Double-check that you selected the station's WiFi, and aren't accidentally using some other nearby WiFi network.
- Open a web browser and browse to: https://test-ipv6.com/
WARNING: That link is a third-party website NOT controlled or warranted by AngelTrack LLC. - Write down the IPv4 and/or IPv6 address that it reports for you. If it also reports any warnings regarding your internet connection, copy them into an email and send it to your IT department for review.
- Login to AngelTrack with HR, Captain, and/or Administrator privileges.
- Go to Settings and select the "Timeclock Hosts" item
- Add the IPv4 and/or IPv6 addresses as an allowed clock-in location, and list them under the station's name. For each address, you will list only the first half; for example:
- If your IPv4 address is 12.34.56.78, then list only the first two segments: 12.34
- If your IPv6 address is 2600:387:ab:09::e1, then list only the first three segments: 2600:387:ab
- Be sure to disable the built-in "All IP addresses" entries so that your restrictions will take effect.
Your IT department will understand this issue, so please ask them to set this up for you, or to review your work.
IPv6 Address Requirements
If your station's internet connection has an IPv6 address, then you must add it to the list, regardless of whether it also has an IPv4 address. This is because any device using your station's internet connection might connect to AngelTrack using the IPv6 address, rather than the IPv4 address; there is no way to control which address a connected tablet or workstation will choose to utilize.
It is not necessary for your stations to have IPv6 addresses, because AngelTrack supports IPv4 too, but if you do have one, then it must go into the list.
To see which IPv4 and IPv6 address your internet connection has, visit https://test-ipv6.com….
Internet connections with no IPv6 address
If your station's internet connection has no IPv6 address, then AngelTrack will see only IPv4 connections coming from it. In that case, only the IPv4 addresses in AngelTrack's allowed list will be relevant.
Away from the station, where clock-in is not allowed, it does not matter whether your devices have IPv4, IPv6, or both addresses.
Be warned: If your station's internet connection does not yet have an IPv6 address, it could get one at any time. It is entirely up to your ISP. On the day they finally issue you one, and the computers at the station begin to use it, they will be unable to clock-in until you add the IPv6 address to AngelTrack's list.
Static and Dynamic IP Addresses
If your station's internet connection has its own static IP address, then simply input that address into AngelTrack as an approved clock-in location. A static IP address is guaranteed to never change, so you're all done.
Most stations do not have a static IP address. Instead they have a dynamic IP address, also known as a "DHCP address". Dynamic IP addresses change over time. They usually change once a week, or perhaps once a month. One week it might be 198.51.100.65, and then the next week it might be 198.51.51.188.
The assigned addresses are random, but they will always fall within a certain range. In this example, the range is probably 198.51.something.something.
You can configure AngelTrack to allow clock-in from any address within that range: simply input the first half of the address ("198.51" in this example) as the allowed IP address. AngelTrack will add "/16" to the end, indicating that only the first 16 bits (i.e. only the first half) of the address must match. (The "198" in this example is 8 bits and the "51" is another 8 bits, 16 bits total.)
The same applies to IPv6 addresses, if your internet service has made the switch. The Time-Clock Hosts list accepts IPv6 addresses just like traditional IPv4 addresses, except that an IPv6 address must contain at least one colon (:) character. You can still specify a partial address, with or without a /bits value.
Don't be fooled by your NAT address
Most company networks use a NAT router, which means that computers on your local network do not know their real IP address as seen from the internet. If you ask your computer for its IP address, it will respond with "10.1.10.104" or "192.168.0.115" or some such. That is not its real IP address as seen from the outside world. Your computer does not know its real IP address as seen from the outside world.
This is the doing of your internet modem/router -- the device that connects you to your ISP.
Your AngelTrack cloud server is on the internet, and it can therefore see your real IP address; it will be shown as "Your current IP address" on the right-hand side of the page. It is this real IP address, not the artificial NAT address used within your local network, that must be specified as an approved clock-in location.
Checking everyone's IP addresses at once
If you would like to see the IP addresses in use by all of your employees, visit the Heartbeat page under Settings. It lists all employees whose computer or mobile device has interacted with AngelTrack within the last two minutes.
You can click any IP address in the list to check which ISP it belongs to. You will probably see some employees at your station, and other employees on cellular (mobile) networks. It is the station's IP address that goes into the list of timeclock hosts.
Does Your ISP Change Your IP Address Too Often?
If your ISP keeps changing your IP address, and you are tired of adding more and more entries to this list, then call your ISP and rent a static IP address.
They usually cost just a few dollars per month, and they are guaranteed to never change. In fact you can specify the exact address they assign, rather than a range (/16 or /24) of addresses.
Setting Up Other Timeclock Locations
If you use restaurants, coffee shops, hotels, libraries, or fire stations as posts, you can allow employees to use the timeclock from there. Simply visit the location, connect to their WiFi, and add their internet address to the list exactly as you did for your own station.
Be sure to give each location a descriptive name, so that you can disable and enable them later, as your posts change.
If a location does not have a static IP address, then you will have to put up with it changing from time to time, as discussed above.
Exempting Certain Trusted Employees
You can exempt individual employees from these restrictions, allowing them to clock-in and clock-out wherever they please.
Visit the employee's Employee File page and select the "Privileges" tab. You must be a member of HR or an Administrator to grant or revoke the privilege.
Restoring the Timeclock's Unrestricted State
When initially deployed, AngelTrack allows unrestricted clock-in and -out. This is done using a pair of "all IP addresses" entries in the list, one for IPv4 and one for IPv6. Best practice is to deactivate these two entries and set up a restricted list, as shown in the screenshot above.
If you later wish to bring the unrestricted entries back, simply re-activate them: untick the ☑ Hide inactive hosts checkbox, find the "All IPv4 hosts" and "All IPv6 hosts" entries, and reactivate them.
Troubleshooting / Cannot Clock In
If one morning everybody cannot clock in, then probably your ISP has changed your IP address, and so you must repeat the process above to add your station's new IP address(es) to AngelTrack's list of approved locations.
If only a certain employee cannot clock in, then verify each of these:
- Double-check that their mobile device is connected to the station's WiFi access point. Make sure they didn't accidentally connect to another nearby WiFi access point.
- If they are definitely connected to the correct WiFi access point, but still cannot clock in, then visit the Heartbeat page (under Settings), find the employee's AngelTrack login in the list, and note the IP address they are using to connect. Then return to the timeclock allowed IP list, and verify that their IP address is in the list, following the instructions above for entering just the first one-half (or the first one-third for an IPv6 address) into the list of permitted addresses. Situations like this can arise when one employee's device utilizes an IPv6 address while everyone else's devices were utilizing IPv4 addresses, and so once you add the IPv6 address to your list, it will work.
- Using their mobile device, browse to https://test-ipv6.com/ to double-check their reported IP address, as well as check for any networking problems such as IPv6 MTU failures.